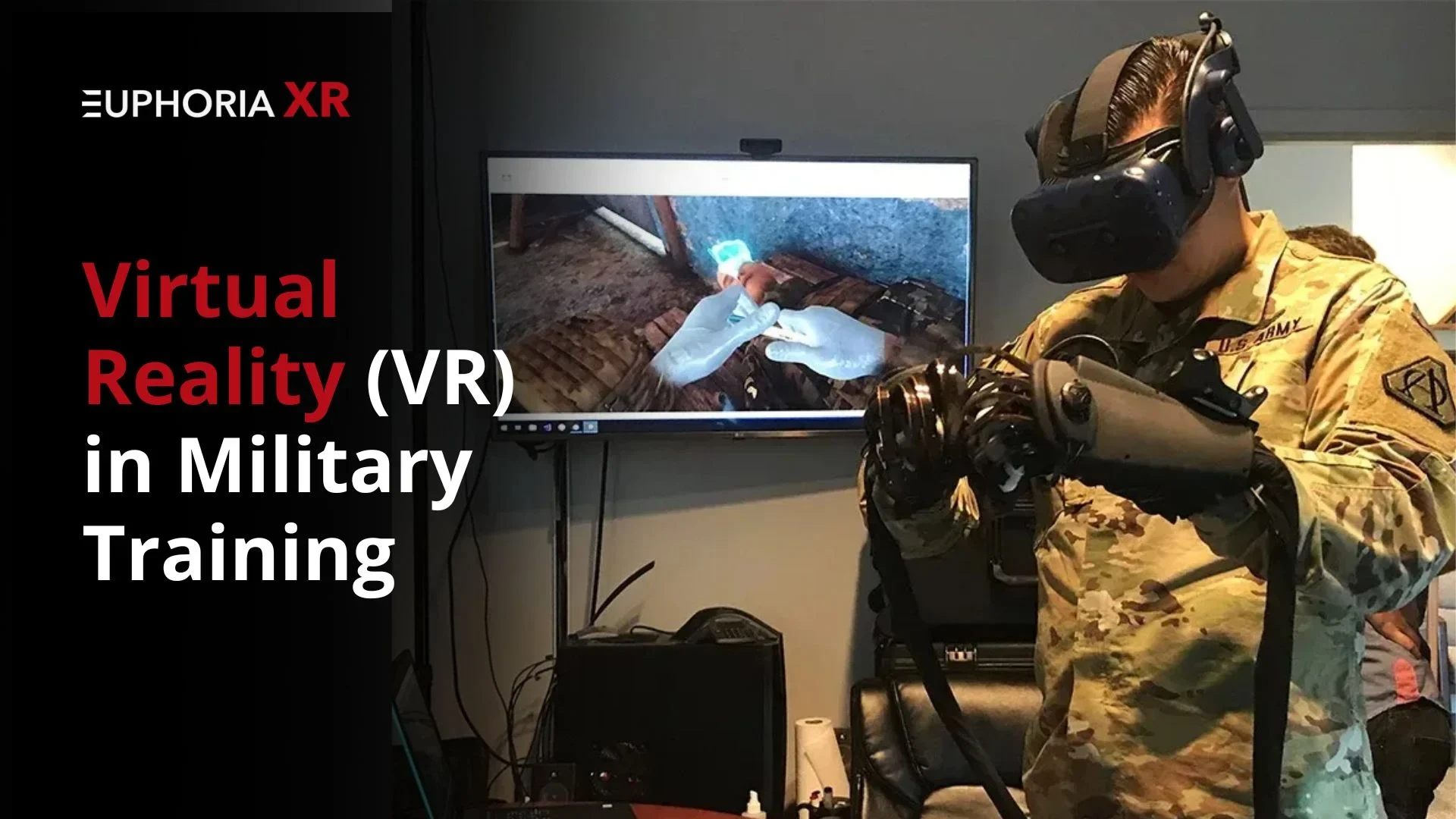
Safer Training, Stronger Soldiers – How VR in Military is Shaping the Future
Think of entering a battleground without ever leaving a room.
Without the dangers of actual conflict, you are in a high-stakes combat situation, avoiding bullets, planning with your squad, and feeling the ferocity of battle. Science fiction is not what this is. Virtual reality (VR) in Military Training is revolutionizing how soldiers train for combat, manage stressful situations, and even heal from trauma.
Virtual reality in military training is just another example of how the military has always been a pioneer in implementing new technologies. VR is giving soldiers all across the world safer, more affordable, and more immersive training options for everything from medical training to combat simulations.
Let us examine how VR is changing defense tactics in military applications, supported by empirical data and real-world examples.
The Evolution of VR in Military Training
Virtual reality in the military has been developing for many years. VR continues the tradition of early military adoption of innovative technologies. Let us examine the evolution of virtual reality in military training.
1. Early Beginnings (1960s–1980s): The Birth of VR in Military
- To train Air Force pilots, the military originally experimented with virtual reality concepts in the 1960s using flight simulators.
- Link Trainer, a mechanical flight simulator that trained pilots without the risk of the actual world, was one of the first examples.
- Research on simulation-based training was first funded by the U.S. Department of Defense in the 1970s.
- To replicate space conditions, NASA created the first VR-based astronaut training modules.
2. VR Expansion in the 1990s: Rise of Immersive Military Simulations
- As computers became more powerful, VR development exploded in the 1990s.
- To help soldiers learn combat tactics without using live weapons, the U.S. military implemented virtual reality (VR) for battlefield simulations.
- Infantry troops can now train in virtual combat settings thanks to the introduction of Dismounted Soldier Training Systems by the Army and Marine Corps.
- Officers were able to practice strategic movements by integrating virtual reality (VR) into tactical decision-making systems.
3. 2000s–Present: Advanced Integration of VR in Military Training
- The development of graphics and artificial intelligence (AI) led to the hyper-realism of military virtual reality systems.
- The U.S. Army, Navy, and Air Force spent billions on creating medical simulations, vehicle simulators, and virtual reality combat training.
- To improve situational awareness and combat effectiveness, the U.S. Army and Microsoft inked a $22 billion agreement in 2021 to develop mixed reality headsets based on HoloLens.
- Full-body tracking suits, haptic feedback, and real-time AI-powered combat scenarios are all examples of virtual reality in military training today.
The development of virtual reality in military training demonstrates that VR is now an essential part of contemporary defensive tactics and is no longer merely a futuristic instrument.
Applications of VR in Military Training
The use of VR technology in the military has expanded beyond combat simulations. Let us examine each of the main applications of VR in the military today.
1. Combat Training Simulations
Preparing soldiers for unforeseen combat scenarios is one of the most difficult aspects of military training. Virtual Reality in Medical Training enables soldiers to experience realistic warfare situations without being exposed to actual threats. Through these simulations, soldiers can refine their teamwork abilities in stressful situations, increase their tactical awareness, and enhance their ability to make snap choices.
Multi-user virtual reality battlefields allow soldiers to train together from many places, improving unit coordination and communication. The versatility of virtual reality combat training allows for the programming of various battlefields, adversary strategies, and mission objectives to replicate the realities of contemporary conflict. Research indicates that troops who receive tactical training based on virtual reality (VR) make strategic decisions 30% more quickly than those who receive instruction with conventional techniques.
Example:
The Synthetic Training Environment (STE), a state-of-the-art virtual reality system used by the U.S. Army, allows soldiers to practice in three-dimensional virtual combat zones. It combines full-body motion tracking, haptic feedback suits, and AI-powered opponents in real time to provide an incredibly engaging and productive training environment.
2. Flight and Vehicle Simulators
Extensive training is necessary to operate military aircraft and armored vehicles, and errors made during practical training exercises can be costly and hazardous. VR flight simulators offer a realistic, affordable, and safe substitute for traditional methods of training pilots and vehicle operators.
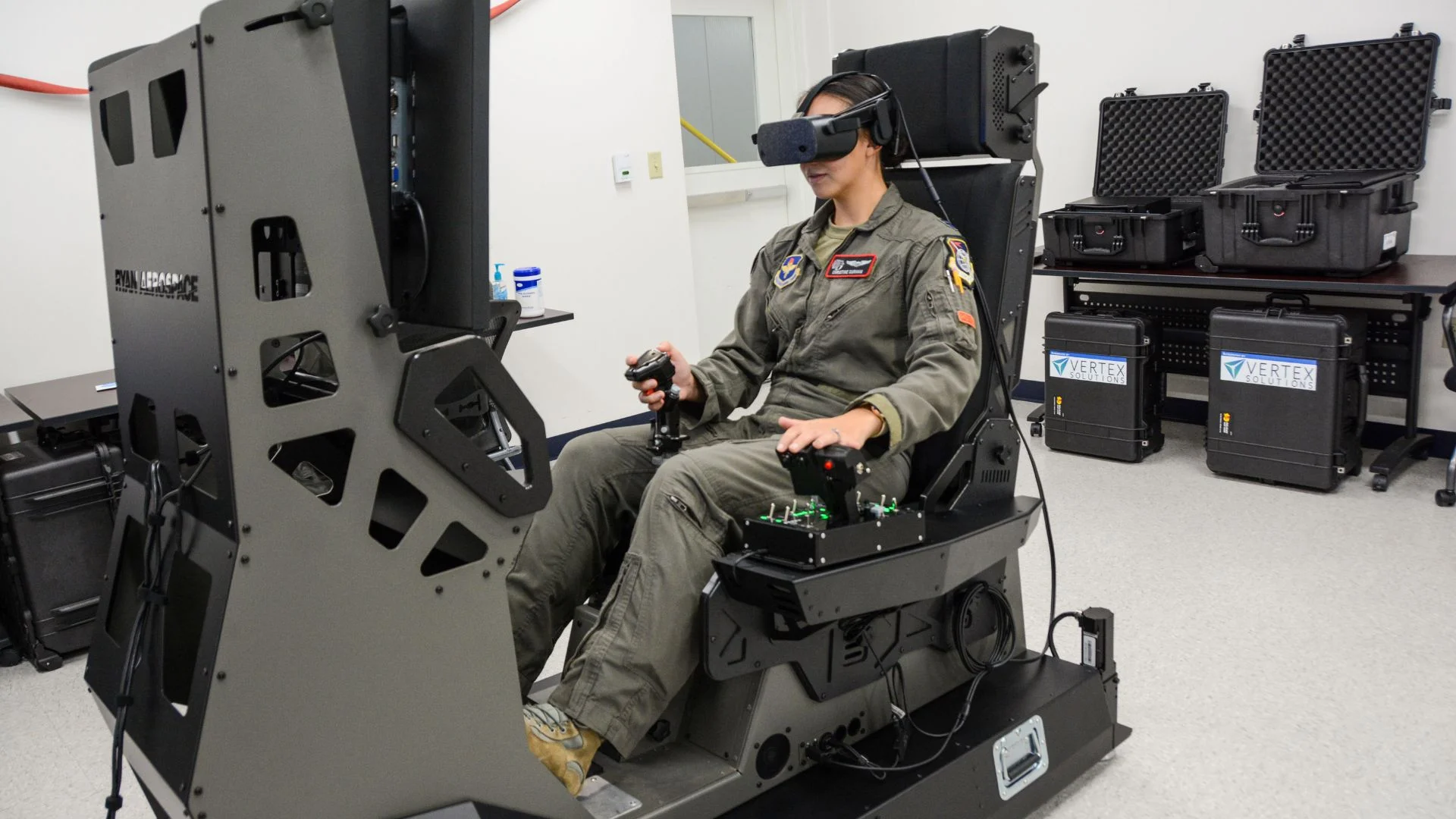

In a virtual cockpit that simulates actual conditions, pilots can rehearse emergency landing techniques, aerial combat, and aircraft maintenance. Additionally, before ever stepping foot in a real vehicle, ground troops and naval officials can practice on tanks, armored vehicles, submarines, and warships using virtual reality (VR).
Example:
The Pilot Training Next (PTN) program of the U.S. Air Force has included virtual reality headsets in fighter jet training, which has resulted in a 50% cost reduction when compared to conventional simulators. Pilots can rehearse emergency procedures and hazardous combat maneuvers with these virtual reality systems without endangering costly aircraft or human lives.
3. Battlefield Medic Training and Emergency Response
Medics in battle zones have to make snap judgments that could save lives. Any mistake or hesitation could be fatal. By modeling trauma care scenarios in real-time, virtual reality (VR) in military training has completely changed how medical personnel and battlefield medics prepare for war-related injuries.
Medics can practice treating severe wounds, managing mass casualty crises, and making critical medical decisions using virtual reality-based emergency response training. Medical teams can improve overall patient survival rates by reducing errors by 30% with the use of virtual surgeries and medical simulations.
Example:
The Tactical Combat Casualty Care (TC3) VR program of the U.S. Navy enables medical professionals to treat virtual patients while simulating battlefield situations and providing real-time feedback. Medical professionals can practice applying tourniquets, controlling
bleeding, and performing emergency procedures under pressure by interacting with realistic virtual casualties.
Suggested Read: https://euphoriaxr.com/virtual-reality-in-medical-training-education/
4. Equipment Maintenance and Repair Training
Modern military operations depend on sophisticated equipment, such as sophisticated weapons and airplanes. Maintenance errors can result in equipment damage, mission failures, or even fatalities if sufficient training is not received. By enabling engineers and troops to learn how to install, disassemble, and repair military hardware in a virtual setting, virtual reality (VR) has revolutionized equipment maintenance training.
Trainees can investigate the workings of different pieces of equipment by using interactive 3D models, which lowers the possibility of causing damage to actual assets. By cutting training time by 40%, VR-based aids enable staff members to learn more quickly and accurately.
Example:
Lockheed Martin’s virtual reality maintenance training reduces human error and ensures that military equipment is always in top condition by increasing repair efficiency by 50%.
5. PTSD Treatment and Rehabilitation for Veterans
Long-lasting psychological and bodily wounds are caused by war. Many soldiers struggle to adapt to civilian life because they suffer from Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). With secure, regulated settings that allow veterans to face their trauma at their own pace, virtual reality (VR) has become a popular technique for PTSD treatment.
Under the supervision of mental health specialists, patients can experience traumatic events in a therapeutic environment via VR-assisted cognitive therapy. Veterans’ anxiety and depression are lessened by relaxation techniques, meditation settings, and virtual social reintegration scenarios.
Example:
A Harvard Medical School study discovered that VR-based PTSD therapy is one of the best non-pharmacological treatment choices for veterans, reducing symptoms by 56%.
6. Military Mission Planning and Strategy Development
Military leaders can use virtual reality (VR) to build digital twins of actual battlefields, which facilitates strategic planning and mission practice before deployment. To assess potential outcomes and improve tactics, troops can simulate operations in real time.
Military leaders can forecast enemy movements, test alternate tactics, and increase operational success rates by examining numerous war scenarios. Additionally, military strategists can test out various strategies without putting lives in danger by using virtual war games.
Example:
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is testing novel military tactics through AI-powered virtual reality simulations, increasing the efficacy of contemporary fighting.
7. Cybersecurity and Digital Warfare Training
Cyberwarfare has emerged as one of the most significant risks to national security due to the growing dependence on digital infrastructure. To protect communications, intelligence networks, and vital defense systems against cyberattacks, military intelligence services are always on the lookout. To help professionals train in digital warfare and cyber threat response, virtual reality (VR) is increasingly being employed in military training to replicate actual cyberattack scenarios.
How VR Aids in Cybersecurity Training:
By simulating real-time cyberattacks in a safe setting, virtual reality (VR) teaches cybersecurity experts how to identify threats, minimize damage, and stop future intrusions. Teams are prepared for high-pressure digital warfare scenarios via this practical experience.
Hacking and Defense Techniques:
Cybersecurity experts prepare for cyberwarfare in the same way that soldiers do. Teams can test various hacking methods and create defensive countermeasures to stop network invasions with the use of virtual reality.
Digital War Exercises:
By simulating multi-player cyberwarfare, virtual reality (VR) helps businesses better grasp how contemporary cyber wars play out.
Example: The VR Training Labs of U.S. Cyber Command
VR-based cybersecurity training laboratories have been set up by the U.S. Cyber Command to mimic hacking situations and cyber defense drills. The military’s digital infrastructure is kept safe thanks to these labs, which give security experts the chance to practice protecting against actual attacks.
8. VR in Naval Warfare Training
Comprehensive training in submarine operations, maritime fighting, and emergency protocols is necessary for naval warfare. Naval officers and sailors have always received their training through classroom-based instruction and onboard drills, but virtual reality (VR) has completely changed the process by offering realistic, immersive training experiences without the need for actual ship access.
How Virtual Reality (VR) Enhances Military Training
Submarine and Ship Navigation:
VR allows military officers to experience ship navigation in real-time, including navigating through inclement weather, dodging obstacles, and fighting at sea.
Storm and Battle Simulations:
By using virtual reality naval combat simulations, officers can prepare for hostile attacks, emergency evacuations, and choppy sea conditions. Crews can practice managing high-risk missions with the aid of these simulations.
Crisis Response at Sea:
With realistic emergency simulations, virtual reality (VR) helps naval personnel get ready for ship collisions, natural disasters, and rescue operations.
Example: The Project BlueShark VR Program of the US Navy
For submarine and naval strategy instruction, the U.S. Navy’s Project BlueShark offers a 360-degree virtual reality environment. Officers can practice intricate naval maneuvers to make sure they react to dangers in the real world.
9. Search and Rescue Training
Search and rescue (SAR) missions, in which teams must find and rescue injured soldiers, hostages, or survivors of disasters, are among the most crucial components of military operations. Every second matters in harsh environments, and virtual reality (VR) in military training is assisting SAR teams in increasing productivity, coordination, and reaction times.
How Virtual Reality (VR) Improves Search and Rescue Training
Disaster Response Simulations:
Troops may practice finding survivors and delivering relief in VR-based earthquake, flood, and wildfire scenarios.
Hostage Rescue Training:
By simulating hostage extractions, special forces may hone their negotiation skills, entrance strategies, and extraction procedures.
Drone-Assisted Search Missions:
Drones are used for aerial observation in many contemporary SAR missions. Teams can practice using virtual drones in virtual reality (VR) to identify survivors in hazardous or inaccessible locations.
Example: The VR Rescue Training of the U.S. Coast Guard
To ensure that officers can effectively respond to emergency rescue scenarios both on land and at sea, the U.S. Coast Guard uses virtual reality (VR) to educate officers in harsh weather circumstances.
10. Sniper and Marksman Training
For military marksmen and snipers, accuracy in shooting is crucial. Live-fire drills, a staple of traditional sniper training, necessitate costly ammunition, regulated settings, and particular terrain. By enabling snipers to practice target acquisition, shooting mechanics, and battle placement in lifelike virtual surroundings, virtual reality (VR) offers a safer and more affordable option for military training.
How Virtual Reality Helps Sniper Training
By Simulating Combat Environments:
By simulating different terrains, weather patterns, and lighting scenarios, virtual reality allows snipers to practice in settings that closely resemble actual battlefields.
Ballistic and Moving Target Training:
To improve accuracy, soldiers can practice with VR-based moving targets by modifying their breathing control, aim, and trigger discipline.
Night Vision and Infrared Targeting:
Nighttime is a common time for modern military operations. Snipers can practice using night vision and infrared aiming devices in virtual reality, which guarantees they can engage adversaries in low light.
Example: The VR Sniper Training Program of the British Army
By using VR-based sniper training, the British Army has increased accuracy rates by 35%. Without wasting ammo or needing outdoor training facilities, the training helps soldiers adapt to long-range battles, changing wind speeds, and various shooting positions.
Innovate with Virtual Reality! Being the best Virtual reality development company, Euphoria XR creates top-notch VR experiences for training, education, and entertainment.
Benefits of VR in Military Training

1. Enhanced Safety
Soldiers can practice in hazardous situations without taking any physical risks by using virtual reality training simulations.
2. Cost-Effective Training
Millions of dollars can be spent on live training sessions. In military training, virtual reality dramatically lowers costs associated with:
Wear and tear
Ammunition and fuel equipment
Logistics and transportation
3. Better Retention of Knowledge
When compared to conventional techniques, VR training improves recall rates by 75%, according to research from the University of Maryland.
4. Scalable and Customizable
Military organizations may scale their training across various sites and modify situations for certain operations thanks to virtual reality.
Challenges of VR in Military Training
VR in military training has many drawbacks despite its benefits:
High Initial Costs: Although setting up sophisticated VR systems might be costly, the benefits over time offset the cost.
Technical Restrictions: Motion sickness mitigation, graphical realism, and haptic feedback are still areas where VR technology needs to advance.
Psychological Impact: Soldiers may experience unidentified long-term mental health repercussions from excessive exposure to virtual warfare settings.
The Future of VR in Military Training
As technical developments continue to expand their potential, virtual reality training has a very bright future. The incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI), which will allow VR Simulations to adjust in real-time to a soldier’s behavior, judgment, and fighting skills, is among the most important advancements. As a result, military training will become more dynamic and individualized, enabling soldiers to practice in changing conditions that replicate the volatility of the real world. Furthermore, the use of haptic feedback technology will enhance the immersiveness of VR-based training by enabling soldiers to experience the effects of their surroundings, including weapon recoil, environmental dangers, and even the physical strain of combat situations.
Additionally, by superimposing maps, enemy locations, and real-time data onto a soldier’s field of vision, Augmented Reality (AR) will improve situational awareness when integrated into virtual reality (VR) military systems. Tactical decision-making and battlefield intelligence will be greatly enhanced by this. Another significant breakthrough is the creation of cloud-based virtual reality military training networks, which will facilitate cross-border cooperation and boost military coordination and alliances by allowing soldiers from other countries to train together in virtual joint exercises.
The defense industry is anticipated to be among the largest users of virtual reality technology, with the global market for military training and simulations predicted to reach $11.5 billion by 2025. By 2030, PwC estimates that VR and AR technologies will boost the global economy by $1.5 trillion, with the military and defense industries expected to be among the most affected.VR will continue to push the limits of realism and efficiency in military applications as these technologies advance, making it a vital tool for the future armed forces.
Are you trying to find the best VR developers? Bring your idea to life by collaborating with Euphoria XR.
Final Thoughts!
Virtual reality is already being used in military training; it is no longer a sci-fi idea. Virtual reality (VR) is revolutionizing how soldiers learn, prepare, and recuperate from military service, whether it is through combat training, flight simulations, or PTSD treatment.
We are seeing the next phase of military readiness as international defense agencies spend billions on virtual reality technology. Virtual reality in military training will only get more effective, immersive, and crucial to contemporary defense tactics as technology develops.