How AR is Improving the Safety, Speed, and Intelligence of Healthcare?
Imagine a world in which patients receive real-time diagnosis and treatment plans with 3D visuals, surgeons perform operations with superhuman precision, and medical students practice difficult procedures without the risks of real life.
Thanks to augmented reality (AR) in healthcare, that world is already here and not some far-off future. Medical practitioners can improve everything from surgical accuracy to patient education by superimposing digital images onto real-world situations using augmented reality. By 2026, the global AR healthcare industry is expected to grow to $4.23 billion, propelled by developments in patient monitoring, remote care, and medical education. However, how precisely is AR influencing the medical industry, and what lies ahead? Let us investigate.
What is Augmented Reality(AR) in Healthcare?
A technology called augmented reality (AR) overlays digital content on the physical world. By combining 3D models, medical imaging, and real-time data visualization, augmented reality (AR) improves interactions in the real world as opposed to virtual reality (VR), which provides an entirely digital experience.
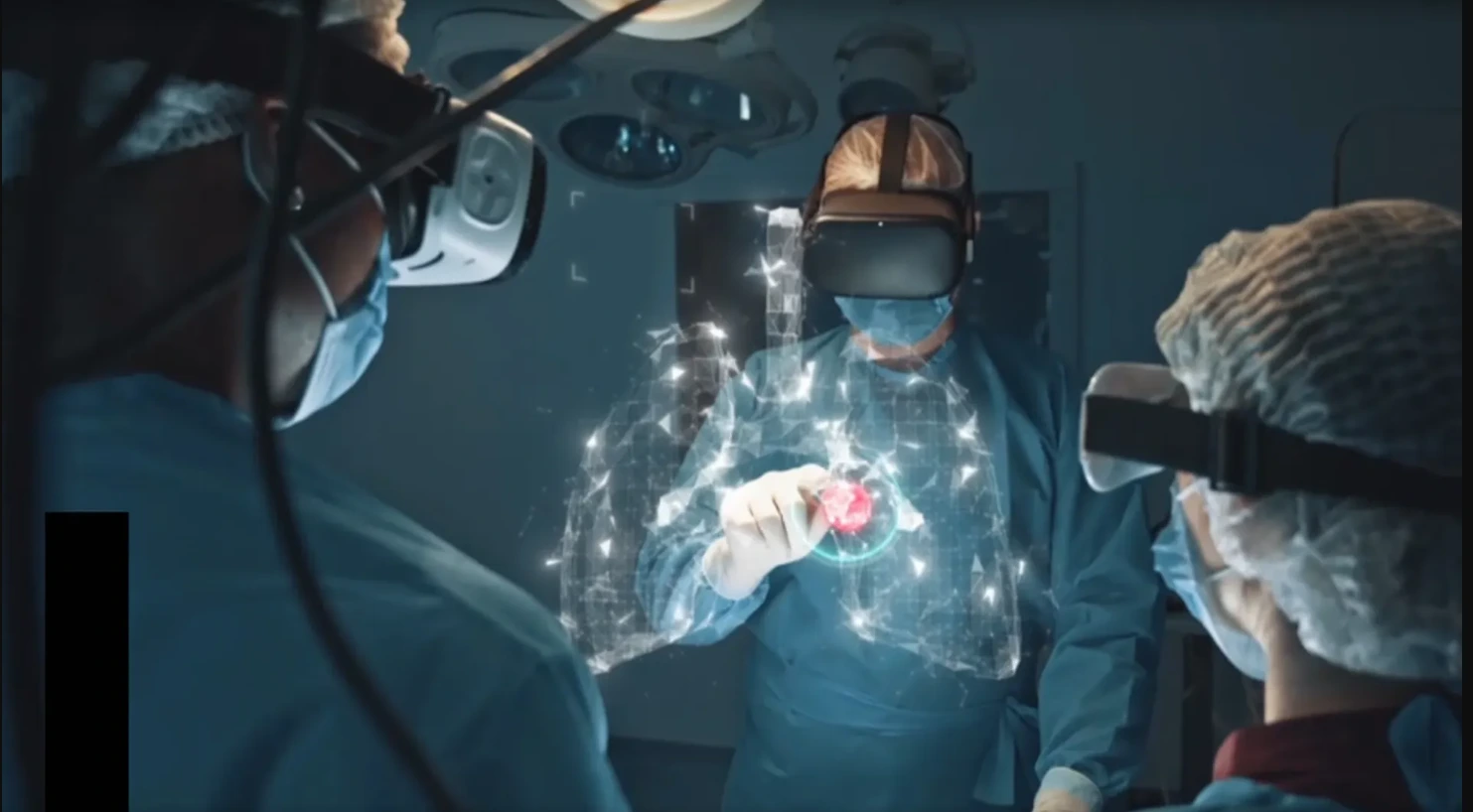
By giving medical practitioners real-time support, augmented reality is transforming surgery, diagnostics, training, and rehabilitation in the healthcare industry. The power of AR in medicine can be seen in situations when a surgeon views a patient’s internal organs in three dimensions before making an incision or when a medical student uses an AR overlay of human anatomy to practice intricate operations.
What is the Impact of Augmented Reality In the Medical Field?
By bridging the gap between the physical and digital worlds, augmented reality (AR) is transforming the medical industry and improving healthcare visualization, accuracy, and efficiency. AR enables physicians, surgeons, and medical students to make smarter, data-driven decisions in real time by superimposing digital content onto the physical world.
Market Analysis: The Growth of Augmented Reality in Healthcare
The Global Market for AR in healthcare is expanding at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 27.4% between 2021 and 2026. The following causes the demand spike:
AR’s growing use in medical procedures
Increasing expenditures on medical education
Developments in patient engagement tools and telemedicine
The necessity of treatment planning and precision-driven diagnosis
The AR healthcare market is predicted to reach over $10 billion by 2030, revolutionizing contemporary medicine.
Augmented Reality in Healthcare: The Most Impactful AR Trends
1. AR-Assisted Surgery & Surgical Planning
Extreme precision is necessary for surgical procedures, and even the smallest error in judgment can have serious consequences. By allowing physicians to view intricate 3D anatomical features superimposed on the patient’s body in real time, augmented reality (AR) is transforming surgical procedures. AR provides unparalleled precision during treatments by integrating MRI or CT scan pictures directly into the surgeon’s field of vision, in contrast to standard imaging methods that require doctors to see separate screens.
How It Works: Surgeons can see organs, blood vessels, and bones in real time with AR-powered headsets like Microsoft HoloLens and Medivis SurgicalAR, which eliminates the need for intrusive exploration and lowers the danger of surgery.
Real-World Example: Surgeons at Imperial College London are now using augmented reality (AR) to superimpose tumor areas onto a patient’s body, assisting them in figuring out the safest and most efficient method of removal. In oncology surgeries, where accurate tumor extraction is essential to a patient’s survival, this method is especially helpful.
Why It Matters: Research indicates that AR-assisted operations result in a 20% shorter operating time and increased surgical precision, which speeds up recovery and lowers the risk of problems after surgery.
2. AR in Wound Care & Physical Therapy
It can be challenging to monitor the healing process, particularly for chronic wounds or the recuperation following surgery. With real-time 3D visualization, AR technology is now being used to assist medical professionals in tracking wounds and rehabilitation progress.
How It Operates: Physicians and physical therapists track wound healing, identify infection early, and create personalized rehabilitation programs using AR-enhanced graphics. During therapy sessions, patients can get immediate feedback on their posture and movements, thanks to AR’s interactive movement tracking feature for rehabilitation.
Real-World Example: Using AR-based overlays, clinicians use GIGXR’s HoloPatient app to track and evaluate wounds, eliminating the need for in-person examinations while guaranteeing precise remote patient monitoring.
Why It Matters: Research indicates that patients who use AR-assisted rehabilitation recover 30% more quickly than those who use conventional physiotherapy techniques. AR is increasing long-term recovery results and patient compliance by making treatment more data-driven and engaging.
3. AR in Real-Time Data and Patient Records Accessibility
Accurate and timely access to patient records is essential in the medical field. By enabling clinicians to view medical history, test results, X-rays, and real-time vitals hands-free without having to switch between displays or physical files, augmented reality (AR) is completely changing the accessibility of patient data.
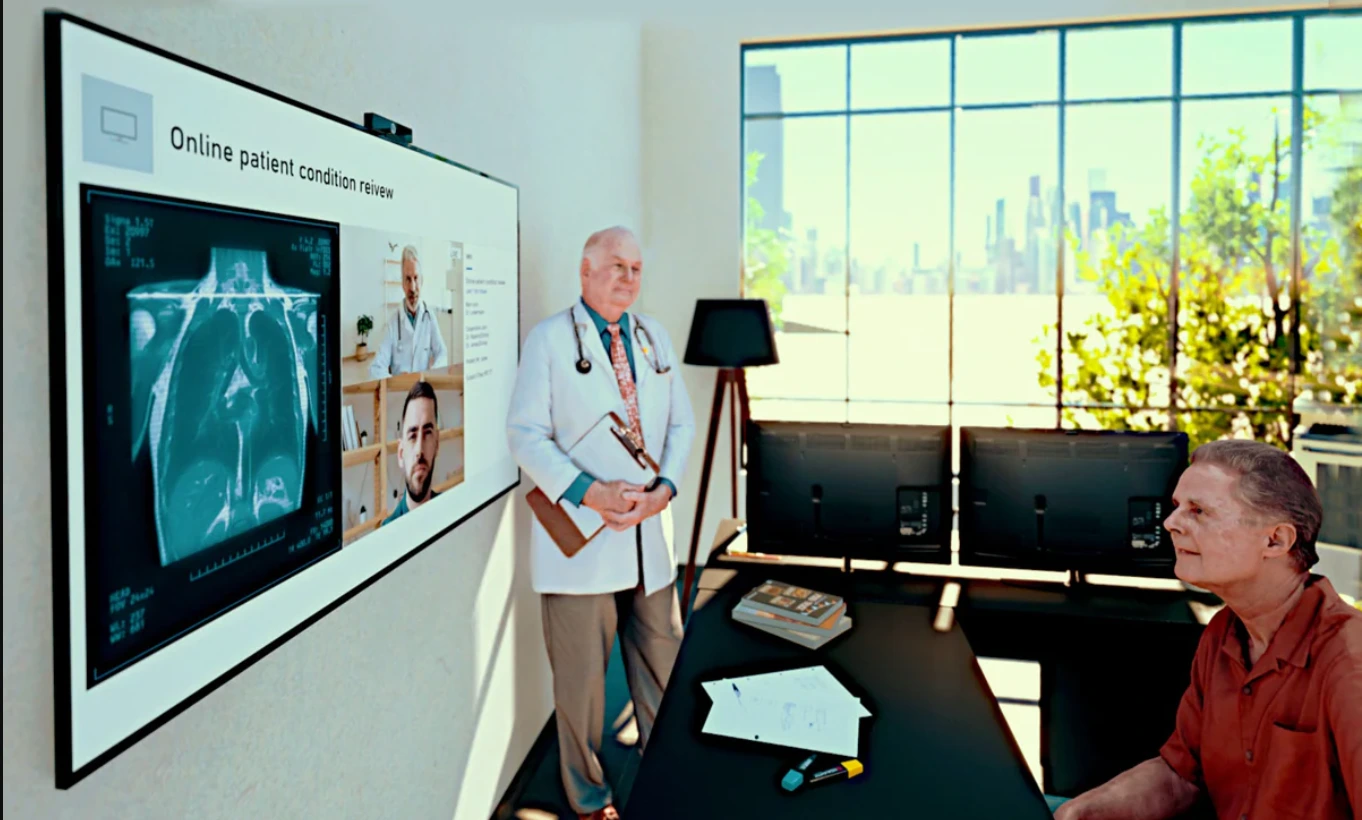

How It Works: Medical practitioners can view real-time overlays of patient data right in their field of vision when they use AR-enabled smart glasses or headsets. During crucial processes, our interactive AR dashboards improve decision-making and decrease errors by updating instantaneously.
Real-Life Example: According to a Duke University Medical Center study, surgeons who used AR-based patient record overlays during procedures cut down on the amount of time they spent going over medical histories by 40%, increasing surgical efficiency overall.
The Significance of It:
Improves monitoring in real-time during operations.
Lowers the possibility of medical errors brought on by lost or out-of-date paper records.
Expedites clinical judgment, particularly in emergencies.
4. AR in Seamless Hospital Navigation
Both patients and medical personnel may find it difficult to navigate hospitals due to their size and complexity. Particularly for first-time visitors, an unclear design can cause annoyance, tension, and delays in care.
How It Operates: Using smartphones or AR smart glasses, AR-based hospital navigation helps patients and visitors make their way to consultation rooms, emergency rooms, or particular facilities by superimposing directional instructions over the actual surroundings.
Real-World Example: Stanford Hospital has reduced patient tardiness by 18% and increased overall hospital efficiency by implementing an AR-powered navigation system that offers step-by-step instructions inside the facility.
Why It Matters: Fast navigation can save lives for medical personnel. In an emergency, physicians and nurses can use AR navigation tools to determine the quickest path to operating rooms, critical care units, or equipment storage places.
Popular Uses of AR in Healthcare Today
1. AR in Bioinformatics, Medical Research, and Pharma
Data visualization is essential to medication development and medical research, and AR is advancing this field. Developing novel drugs and comprehending illness mechanisms is made easier by scientists’ ability to engage with 3D molecular structures and examine genetic sequences in an immersive manner.
How It Operates: By enabling researchers to work with molecular models in three dimensions, AR improves bioinformatics research and offers a more profound comprehension of medication interactions and illness progression.
Real-World Example: To help diagnose genetic problems more quickly, MIT researchers created an AR bioinformatics tool that improved gene sequencing accuracy by 40%.
2. AR in Pharmaceutical and Medical Marketing
AR is being used by pharmaceutical companies to show the efficacy of their drugs in ways that were previously impossible. AR simulations let patients and physicians view inside the body and understand how a drug interacts with cells and organs, eliminating the need for spoken explanations of how a treatment works.
Real-World Example: Pfizer improved patient comprehension and physician engagement by introducing an augmented reality (AR)–powered “inside-the-body” experience that demonstrated how their drugs interact with viruses and cancer cells.
Why It Matters: Research indicates that AR-powered drug education boosts patient adherence by 45% since it gives them greater assurance about their treatment regimens.
3. AR-Based Telemedicine and Remote Healthcare
By offering more precise and immersive remote consultations, augmented reality (AR) is helping to close the gap between patients and doctors, as telemedicine has grown by 63% since 2020.
How It Works: By employing 3D anatomical overlays to aid in diagnosis and treatment planning, doctors can remotely evaluate patients using augmented reality.
Real-World Example: Nurses can find veins remotely thanks to AccuVein’s AR technology, which improves virtual consultations for home healthcare patients who require IV therapy or injections.
Why It Matters: By lowering hospital visits by 25%, remote AR diagnostics can improve access to healthcare and ease the burden on healthcare institutions.
4. AR in Prenatal, Neonatal, and Postnatal Care
To protect the health of both mother and child, close observation is necessary during pregnancy and the care of the infant. By providing real-time fetal imagery, directing prenatal education, and aiding in neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) management, augmented reality (AR) is enhancing maternal and newborn healthcare.
How It Operates:
Expectant women can view 3D interactive models of their unborn child inside the womb thanks to augmented reality.
AR can help doctors schedule required medical procedures by detecting fetal problems early.
AR helps in real-time organ development and vitals monitoring for preterm infants in the NICU.
Example from Real Life:
To facilitate safer deliveries, obstetricians at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center employ augmented reality (AR) to let them visualize the position of the fetal and umbilical cord.
The Significance of It:
Gives parents a more immersive view of their unborn child, which increases parental engagement.
Lowers the possibility of birth issues by carefully evaluating the fetus.
Enhances postnatal surveillance, guaranteeing optimal care for babies.
Are you trying to find a professional AR developer? Virtual simulations, medical education, and augmented reality apps are EuphoriaXR’s areas of expertise.
Examples and Real-World Uses of AR in Healthcare
1. AR in Medical Training and Education
The use of cadavers, textbooks, and 2D imaging in traditional medical education frequently restricts students’ comprehension of intricate anatomical features and surgical methods. By providing interactive 3D models that students can modify, analyze, and study in real time, augmented reality is revolutionizing medical education.
How It Works: Surgeons-in-training and medical students can virtually study human anatomy, conduct simulated surgeries, and practice difficult procedures without taking any risks by using augmented reality goggles or programs.
Real-World Example: Western Reserve University offers students an immersive anatomy lab using HoloLens AR technology, which enables them to interact and inspect 3D models of muscles, blood arteries, and organs in great detail.
The Significance of It:
Enhances skill development and learning retention.
Removes the need for cadavers, which lowers training expenses.
Enables remote learning, opening your access to top-notch education everywhere.
2. AR for accurate Symptom Detection and Patient Self Care
Patients frequently find it difficult to decide if they need medical help for their symptoms. AR-based self-diagnosis tools save needless hospital visits by enabling patients to evaluate their symptoms using AI-driven AR overlays and real-time body scans.
How It Operates:
Patients scan afflicted areas with AR-powered smartphone apps to get real-time medical insights.
AR-enhanced diagnosis apps make recommendations about whether to seek professional care based on a comparison of symptoms with medical databases.
Real-World Example: In just a few minutes, the Ada app provides individualized health assessments by combining AI and AR to evaluate symptoms reported by patients.
The Significance of It:
Saves time and money by cutting down on needless ER visits.
Promotes early health condition detection, which results in prompt treatment.
3. AR for Vein Visualization
It might be difficult to locate veins for IV insertions, injections, or blood draws, particularly in individuals with deep or thin veins. Augmented Reality Vein Finder and imaging decrease the chance of unsuccessful needle insertions, increase accuracy, and lessen patient discomfort.
How It Operates: Healthcare professionals can see the ideal insertion sites by projecting a real-time vein map onto the patient’s skin using handheld augmented reality devices or smart glasses.
Real-World Example: By improving vein visibility by up to 45%, the AccuVein AR scanner lowers the risk of IV insertion errors and lessens the discomfort associated with blood draws.
The Significance of It:
Lowers the number of IV insertion mistakes made by elderly and pediatric patients.
Finds veins rapidly, saving time in emergencies.
4. AR for Medical Imaging
Medical imaging is essential for surgery, therapy planning, and diagnosis. By providing 3D interactive overlays, AR is improving MRI, CT, and ultrasound imaging and enabling real-time internal organ and tissue analysis by medical professionals.
How It Operates: By projecting medical scans onto a patient’s body, AR enables physicians to diagnose diseases without the need for extra imaging procedures.
Real-World Example: Surgeons at Johns Hopkins Hospital employ AR-based 3D imaging to precisely plan neurosurgical treatments and detect brain cancers.
The Significance of It:
Reduces the need for repeated scans, which lowers radiation exposure.
Improves tumor identification and tissue differentiation, increasing surgical accuracy.
5. Augmented reality can save lives by showing how to use a defibrillator
Correct use of a defibrillator during a cardiac emergency can make the difference between life and death. AR offers detailed instructions on how to use an AED (automated external defibrillator).
How It Operates: AR-enabled applications superimpose interactive instructions on actual defibrillators to guarantee that the electrodes are positioned correctly and that the shocks are timed.
An Example from Real Life: Users may quickly learn how to provide CPR and AED shocks during medical crises using the HeartStart AR Defibrillator App.
The Significance of It:
Boosts the confidence of bystanders in emergency circumstances.
Increases the chances that sufferers of cardiac arrest may survive.
6. Using Augmented Reality glasses to see the remote patient in 3D
Although telemedicine has made healthcare more accessible, typical video consultations have drawbacks. For example, doctors can only view patients in two dimensions on a screen, which makes it difficult to perform physical examinations. By enabling clinicians to see patients in three dimensions, augmented reality (AR) glasses are revolutionizing distant healthcare by improving diagnosis and treatment plans.
How It Operates:
AR Glasses project a 3D holographic model of a patient’s bodily movements and structure in real time, allowing physicians to interact with it.
Medical practitioners may more precisely assess posture, injuries, and facial expressions with these AR glasses’ depth-sensing cameras than they could with a traditional video call.
Doctors can highlight, zoom in, or rotate particular body parts to enhance patient contact and diagnostic precision.
Example from Real Life: To assess the severity of neurological symptoms and make decisions on urgent care procedures without the need for in-person visits, clinicians at UCLA Health are remotely examining stroke patients in three dimensions using HoloLens AR glasses.
The Significance of It:
Improves telemedicine capabilities, increasing the precision of remote patient evaluations.
Enables medical professionals to assess injury depth, muscle coordination, and movement Abnormalities without having to be physically present.
Allows professionals in many places to collaborate in real-time, improving patient outcomes and guaranteeing the highest quality of care.
7. AR for Motivating runners through zombies
It can be difficult to stay motivated while working out, but gamification is an effective strategy for increasing exercise adherence. By producing immersive, interactive experiences that make jogging and physical activity more interesting, augmented reality (AR) is now revolutionizing fitness.
How It Operates:
AR fitness applications superimpose virtual obstacles, narratives, and challenges on a runner’s surroundings.
To finish missions or avoid simulated dangers, users must run faster or alter their course.
This method increases motivation by turning working out into an adventure rather than a drudgery.
Example from Real Life: To accomplish goals in the well-known augmented reality fitness app “Zombies, Run!” post-apocalyptic game, players have to outrun virtual zombies. Audio cues and visual overlays mimic the sensation of being pursued while they run, promoting quicker, more reliable exercises.
The Significance of It:
Makes exercising more enjoyable, which raises levels of physical activity.
Introduces game-like challenges to increase speed and endurance.
Promotes consistency, which aids consumers in maintaining their exercise regimens.
Suggested Read: https://euphoriaxr.com/work/fitcus-ai-body-tracking-fitness-app/
8. Augmented reality can assist surgeons in the OR
Extreme precision is required during surgical procedures, and even little errors in judgment can have serious consequences. By overlaying patient anatomy in real time, augmented reality technology is now helping surgeons by increasing accuracy and lowering surgical risks.
How It Operates: A 3D model of the patient’s internal organs, tissues, and bones is projected into the surgeon’s field of vision using AR headsets and smart glasses.
Surgeons can view real-time visual overlays on the patient’s body in place of separate MRI and CT images. This speeds up operation, decreases incision errors, and enhances decision-making.
Example from Real Life: Surgeons at Johns Hopkins University successfully performed spinal fusion procedures using AR-guided technology, increasing accuracy by 20% and cutting down on overall operating time.
The Significance of It:
Improves surgical precision, which benefits patients.
Lowers the chance of problems by reducing intrusive exploration.
Integrates real-time patient data straight into the surgeon’s perspective, increasing workflow efficiency.
9. AR for Teaching Kids about the human body
For kids in particular, learning about the human body can be challenging. Children may now interactively examine the human body, thanks to augmented reality (AR), which is making anatomy education more interesting.
How It Operates: Children can explore 3D interactive models of the human body in real time with AR-powered instructional materials. These applications make studying more visual and interesting by enabling students to zoom in on bone structures, circulatory systems, and organs.
Example from Real Life: With just a particular T-shirt and the Curiscope Virtuali-Tee AR app, kids can see a 3D depiction of their anatomy. Kids may bring biology lessons to life by exploring organs, blood flow, and muscles in real time using a smartphone or AR headset.
The Significance of It:
Turns passive learning into an interactive experience, which raises engagement.
Helps kids better retain complicated medical information.
Encourages an early interest in science and medicine by making anatomy education approachable and enjoyable.
10. AR in Mental Health Treatment
AR is currently being used to deliver immersive, exposure-based therapy sessions for those with anxiety disorders, PTSD, and phobias. Traditional mental health therapies frequently struggle with patient participation.
How It Operates:
Through the creation of safe virtual settings, AR treatment enables patients to confront their phobias.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can be used to guide patients when they are gradually exposed to anxiety triggers.
For best results, clinicians can track physiological reactions and modify the treatment in real time.
Example from Real Life: In comparison to conventional approaches, Psious AR Therapy has effectively treated patients with PTSD, social anxiety, and phobias using AR-based exposure therapy, increasing treatment success rates by 35%.
The Significance of It:
Increases the efficacy of therapy by enhancing the immersive nature of treatments.
Gives exposure treatment a secure and regulated setting.
Increases access to mental health services by enabling at-home therapy for those who live far away.
Ethical implications of augmented reality in health care
To protect patient safety, data privacy, and accessibility, ethical issues must be addressed as augmented reality (AR) becomes more widely used in healthcare. Key ethical considerations are as follows:
Patient Data Privacy: To prevent breaches and guarantee HIPAA/GDPR compliance, AR must implement stringent security measures for the sensitive medical data it collects.
Accuracy & Reliability: AR should supplement medical judgment rather than replace it because misaligned overlays can result in incorrect diagnoses.
Cost and Accessibility: Exorbitant prices may prevent wealthier institutions from using AR, leading to healthcare inequities. We need affordable solutions.
Ethics in Medical Training: Informed consent and anonymization are necessary for ethical compliance when using actual patient data in augmented reality simulations.
Over-Reliance on Technology: To avoid mistakes and preserve human oversight, AR should supplement traditional expertise rather than replace it.
Future of Augmented Reality in Healthcare
1. AR in Dentistry & Orthodontics
With AR, dentists will be able to develop real-time 3D models of teeth and gums for accurate treatments, reforming dental diagnosis and treatment planning. As augmented reality technology develops, orthodontists will be able to create more individualized and least intrusive treatment plans, and patients will be able to see their post-treatment results quickly. In the upcoming years, AI-enabled augmented reality may automate diagnostics, eliminating the need for manual evaluations by detecting cavities and misalignments with almost perfect precision.
2. AR for Psychomotor Skills Training
AR will soon provide hyper-realistic, AI-driven training simulations to help trainees and surgeons hone their psychomotor abilities, which are crucial for medical practitioners who need to be able to make precise decisions with their hands. To provide trainees with individualized skill development according to their learning curve, future AR training systems will integrate haptic feedback, real-time performance tracking, and adaptive learning AI. Physical simulation labs may potentially be replaced by AR as it develops, increasing the accessibility and affordability of medical education globally.
How EuphoriaXR Can Help You with AR Services
EuphoriaXR, as a top Augmented Reality Development Company, provides innovative Augmented Reality (AR) solutions that are designed to improve your company’s performance in a variety of sectors. Among our many services are:
Custom AR Development: Creating custom AR apps that complement your particular company goals.
AR gaming development: Creating engaging AR games that will enthrall and involve your audience.
iOS and Android AR app development: Creating smooth augmented reality experiences that are tailored for the iOS and Android operating systems.
Markerless and marker-based AR applications: Creating flexible augmented reality apps with both markerless and marker-based technology.
Web AR development: Making AR experiences that are available through web browsers without requiring app downloads.
3D Animation and Modeling: Use top-notch 3D animation and modeling to improve the realism and attractiveness of your augmented reality applications.
Virtual Tours: Providing clients with immersive experiences through interactive virtual tours.
Branded AR Filters: Creating unique branded AR filters to increase brand interaction on social media
Healthcare, retail, education, real estate, gaming, and other industries are among the many areas in which we have experience. We hope to improve user engagement, optimize processes, and offer creative solutions that distinguish your company in the digital sphere by incorporating cutting-edge augmented reality elements.
Collaborate with EuphoriaXR to turn your concepts into engaging augmented reality experiences that connect with your target market and propel company expansion.
Final Thoughts!
The future of healthcare is being reshaped by augmented reality, from interactive patient education and rehabilitation to extremely accurate procedures. The accuracy of diagnoses, patient outcomes, and overall healthcare efficiency are all being enhanced by the ongoing developments in AR-powered systems.
The advantages of AR in improving medical care, educating future physicians, and expanding access to healthcare greatly exceed the risks, even though there are still issues to be resolved, such as data security, ethical concerns, and financial constraints.
Healthcare will become more accurate, engaging, and patient-focused than ever before as augmented reality technology develops and continues to push boundaries.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Is AR in healthcare safe for patient data?
Yes, but only in the presence of strict data security protocols. To prevent breaches of patient data, hospitals and AR developers need to make sure that end-to-end encryption, HIPAA compliance, and secure access methods are in place.
What are the major challenges of implementing AR in hospitals?
The most significant obstacles consist of:
AR software and hardware are expensive.
Effective usage of AR requires staff training.
The integration enables seamless data access with current hospital systems.
How does AR help in patient education?
By displaying illnesses, therapies, and surgical techniques in a 3D interactive manner, augmented reality (AR) simplifies medical ideas. Better participation and well-informed decision-making result from patients being able to observe the physical effects of their disease.
What’s the difference between AR, VR, and MR in medicine?
Augmented Reality (AR): Enhances real-life experiences by superimposing digital data and visuals on the physical world.
Virtual Reality (VR): Disconnects the user from reality by creating an entirely immersive digital experience.
Mixed Reality (MR): Combines the virtual and real worlds to enable simultaneous interaction with digital and physical objects.
Which healthcare companies are investing in AR?
To improve surgery, diagnostics, and medical education, several top healthcare organizations are investing in augmented reality (AR):
Microsoft: HoloLens for medical education and surgical planning.
Siemens Healthineers and Philips: AR-powered imaging and diagnostics.
AccuVein-AR: For vein vision during IV placements.
Augmedics & EchoPixel: AR for precise surgery and 3D medical imaging.
Vuzix: AR smart glasses for remote patient monitoring and telemedicine.
Intuitive Surgical & Surgical Theater: AR for preoperative planning and robotically assisted procedures.














